In this tutorial, we will provide an in-depth exploration of capacitors, covering their definition, fundamental principles, operational mechanisms, and various types. Let’s get started!
What is a Capacitor?
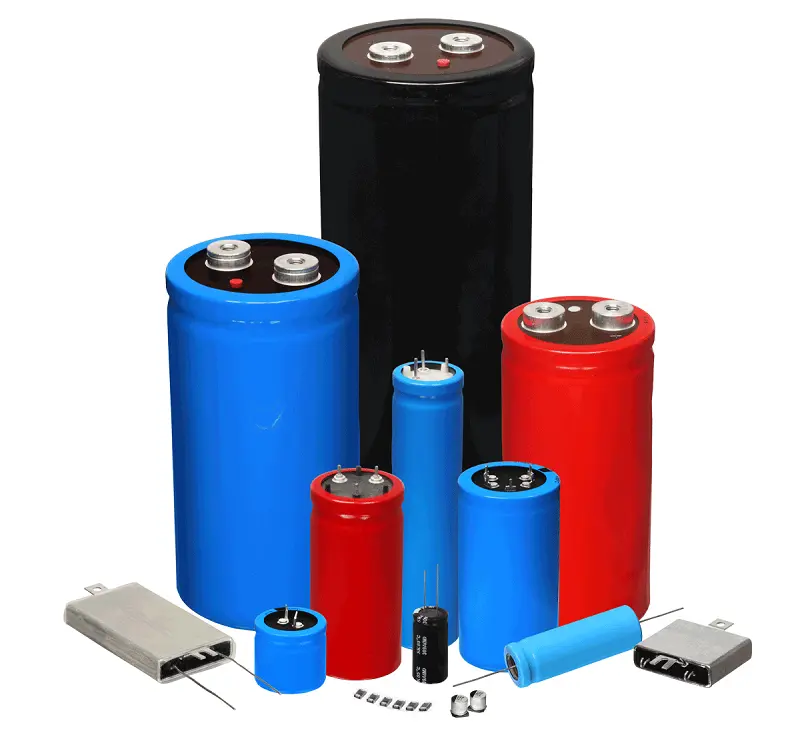
The capacitor is an energy-storing device that stores electrical charges as energy between two conductor plates. An insulating material is placed between two conductors so that charges cannot get from one conductor to another. The capacitor’s capacitance determines how much charge it can store.

Symbol of a Capacitor
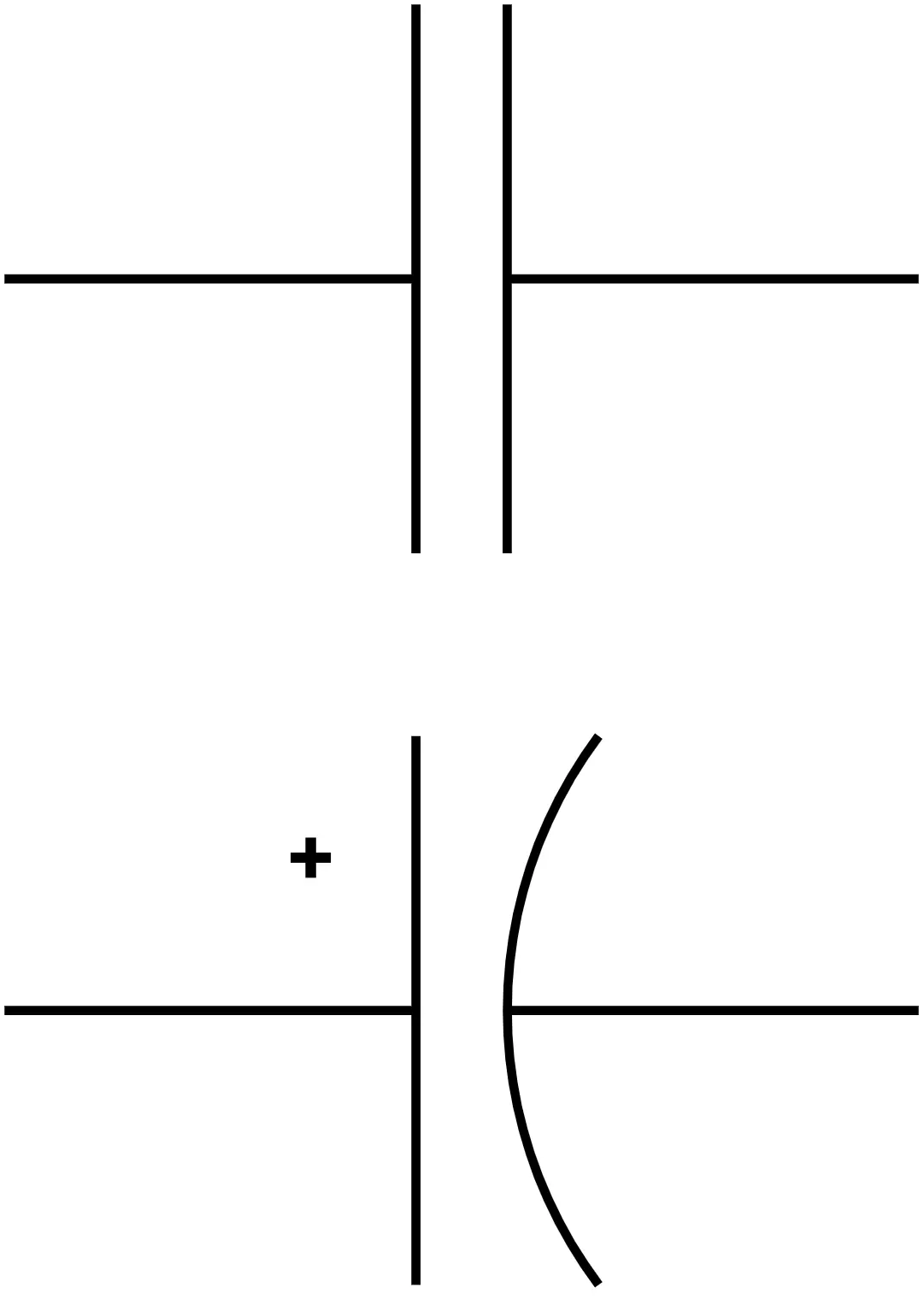
What is capacitance?
The capacitance of a capacitor determines how much charge it can hold per volt. If a capacitor is charged with Q charge and voltage across two conducting plates V is supplied, the capacitance C will be:
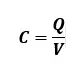
Take note that the total charge should be measured on a single plate.
Capacitance unit
The S.I. unit of capacitance is Farad. It is denoted as F.For example, A capacitor having a capacitance of 10F can hold 10C (coulombs) of charge when a 1V voltage is applied. Other units are mF (Milifarad), µF (Microfarad), nF(Nanofarad), pF (Picofarad), etc.
| UNIT | MULTIPLIER |
| F | 1 |
| mF | 10-3 |
| µF | 10-6 |
| nF | 10-9 |
| pF | 10-12 |
What is the dielectric material?

The capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor
A parallel plate capacitor is constructed using two conductor plates, and a dielectric medium isolates them. The capacitance of a parallel capacitor can be calculated using the flowing equation:
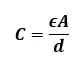

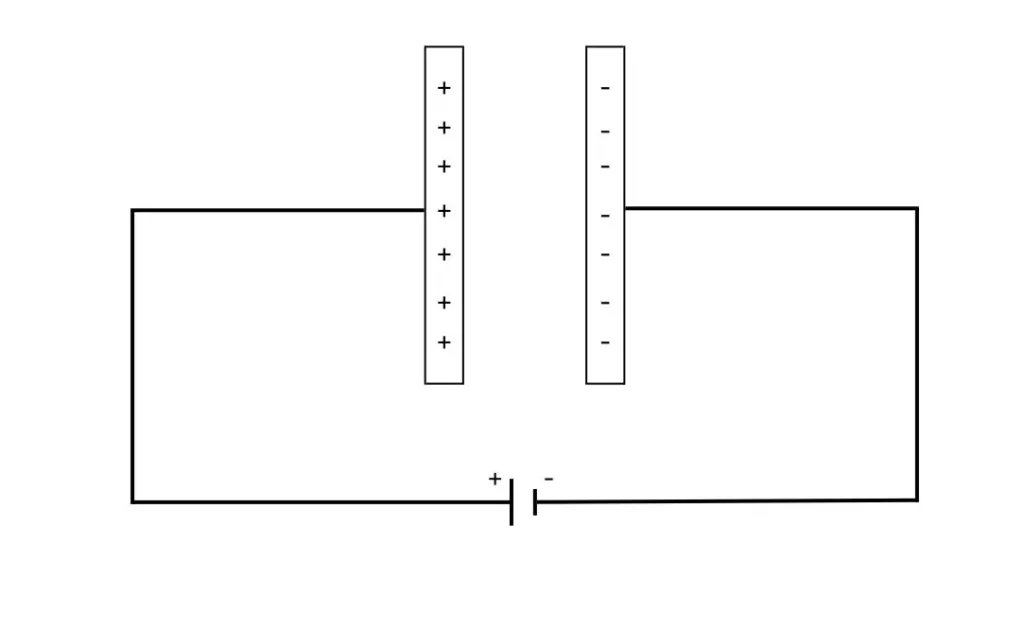
Figure 2: Parallel plate capacitor
How do capacitors work?
Charging
A capacitor typically contains two conductor plates and a dielectric material. When we connect two plates to a circuit, the conductor attached to the positive terminal of the battery is positively charged. In contrast, the conductor connected to the negative terminal is negatively charged. Dielectric material prevents charges from flowing from one plate to another, resulting in an electric field between the two plates. Then this electric field appears as energy. In a DC circuit, when the capacitor gets fully charged no current flows through it and the capacitor is modeled open circuit.
Discharging
When the capacitor is disconnected from the source of the circuit this energy flows back to the circuit. And the voltage across the capacitor decreases. Thus capacitor acts as a temporary source in a circuit.
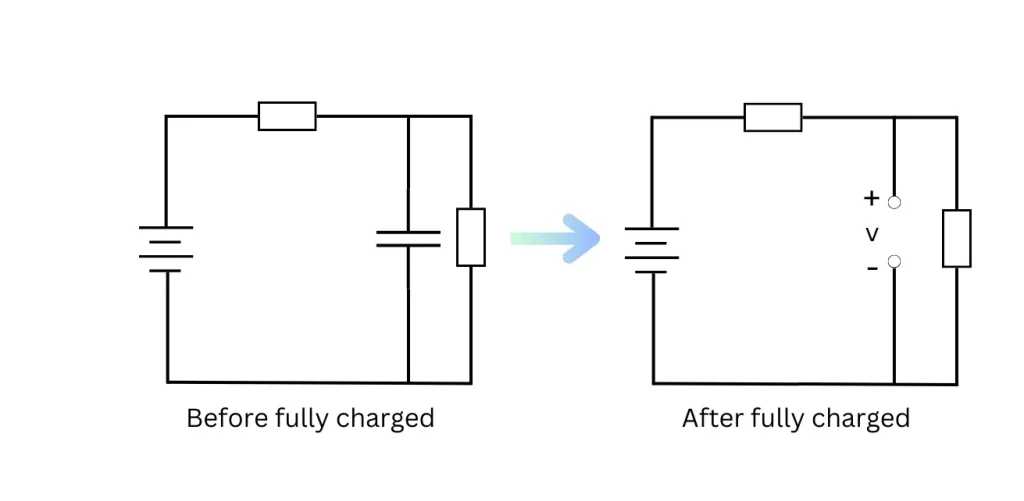
Figure 3: Capacitor in DC circuit before and after fully charged.
How to calculate the energy of a capacitor?
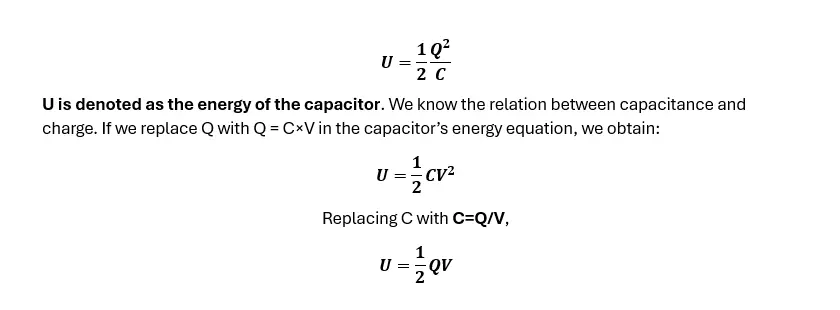
Capacitors hold energy in the form of electric charges. This energy depends on the capacitance of the capacitor. The greater capacitance a capacitor has, the more electric charge it can keep, thus the more energy it can hold. If a capacitor has a capacitance of C, it has been supplied Q quantity of charge therefore V volt potential difference appeared in the capacitor. The equation for the energy of the capacitor will be:
Series/Parallel combination of capacitor
Series combination
The capacitance of capacitors in a series combination is the inverse of the sum of the inverse capacitance. This is the opposite of a parallel combination of resistors.
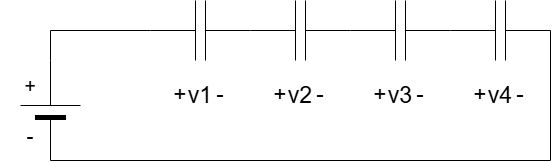
Figure 4: Serial combination
So the equivalent capacitance will be :
1/CEq = 1/C1 + 1/C2 + 1/C3 + …. + 1/Cn
parallel combination
The capacitance of capacitors in a parallel combination is the sum of all capacitance. Hence it is the opposite of a series combination of resistors.
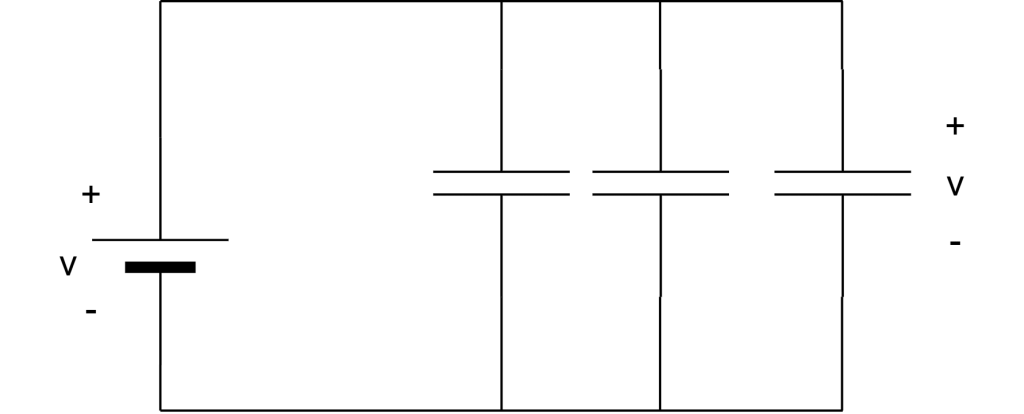
Figure 5: Parallel combination
The equivalent capacitance will be when capacitors are in parallel will be :
CEq = C1 + C2 + C3 + …. + Cn
Types of capacitor
Ceramic capacitors
ceramic capacitor uses ceramic as the dielectric material. They have low capacitance and they are small in size. The capacitance of them ranges from 1nF to 100µF. They are commonly found in electronic circuits.
Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitors
Aluminum foil and aluminum oxide are used as electrolytic capacitors, with the surface rough and a thin layer serving as a dielectric material. These capacitors have high capacitance and voltage ratings.
Tantalum electrolytic capacitors
Tantalum metal is used as the anode and a layer of oxide acts as dielectric in these capacitors. An electrolytic substance is used for the cathode. By construction, this capacitors are polarized. Polarized capacitors are used for high capacitance and for low leakage current. They are commonly used in electronic devices.
Application of capacitors
Voltage regulation
The voltage across the capacitor cannot change instantaneously. That’s why, in a power supply voltage regulator circuits use capacitors for stabilizing voltage.
Decoupling Capacitors
The decoupling capacitor removes noise from the DC signal in the circuit. The decoupling capacitor absorbs unexpected spikes in the voltage of the signal, and if the voltage decreases, the capacitor supplies energy to stabilize it. It is critical for integrated circuits (IC).
Bypass capacitor
A bypass capacitor filters high frequency from the signal. Bypass capacitor gives shortcuts to high frequencies to ground. It is used parallel with the power supply for filtering high frequencies.
Smoothing DC signal
The majority of our household electronics operate on direct current. However, in the supply chain, AC is delivered. Rectifiers convert AC to DC. However, the signal from the rectifier is not smooth and contains unexpected spikes. The capacitor filters the output signal. The capacitor charges as the voltage in the signal increases, and when the voltage in the signal declines, the capacitor prevents the voltage from dropping too low by supplying stored energy. In this approach, the capacitor smoothes the signal and delivers a pure DC signal to the load.
