In this second article of our comprehensive guide on Ethernet communication with Wiznet modules in interrupt mode, we will explore how to send and receive messages between a microcontroller and a computer. To make the process easier to understand, we’ll walk through a hands-on example using the popular STM32 development board, the Bluepill (STM32F103C8T6). For Ethernet connectivity, we’ll be using the widely adopted W5500 module from Wiznet. Interrupt mode will ensure faster communication, suitable for non-blocking requirements.
Understanding the W5500 Wiznet Module
The WIZnet module is a compact Ethernet networking module based on WIZnet’s W5x00 series chips (e.g., W5500), providing a hardwired TCP/IP stack for easy integration with microcontrollers via SPI. It allows stable, low-resource Ethernet communication with support for multiple sockets, ideal for IoT and embedded systems needing reliable wired networking.
The WIZnet module works by offloading all TCP/IP networking tasks onto its built-in hardware chip (like W5500), so your microcontroller just sends and receives data over SPI. The microcontroller tells the WIZnet chip to open a socket, connect to a server (or listen), and send/receive data. The chip handles all the protocol layers (TCP, UDP, IP, etc.) internally, so your code stays simple and fast, without needing a software TCP/IP stack.

To understand more about how this module works, here is a datasheet for the module
Sending and Receiving Messages via W5000: The Project
We will be sending data from a PC to the MCU and vice versa. The communication will be in interrupt mode this time. We will be working on a pre-established library of this module and try to interact using the STM32 microcontroller. Before proceeding, please download apps like Hercules to be able to communicate with the chip via ethernet.
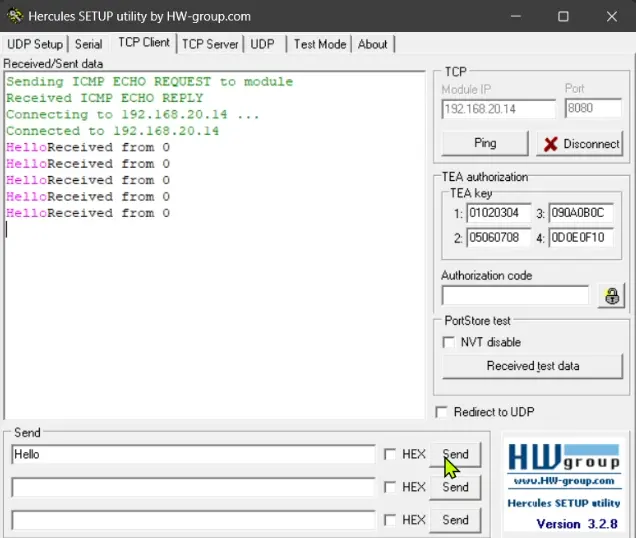
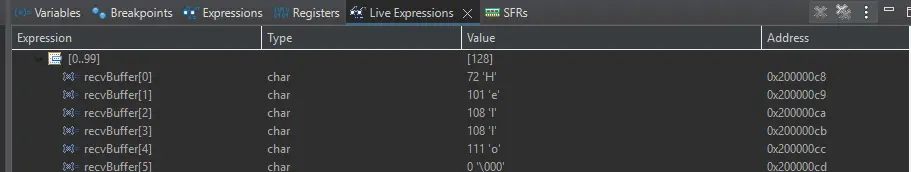
In our project, we will be storing incoming data from the PC to the MCU in a buffer. It will look like this:
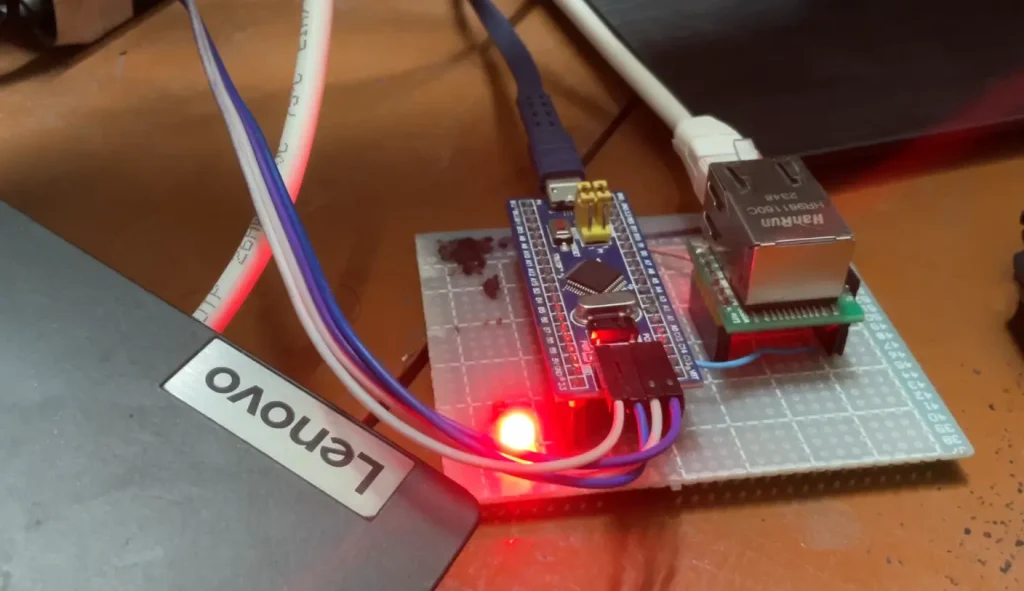
And below there is a hardware prototype where there are additional features and functions.
Component List
| Component Name | Quantity | Purchase Link |
| STM32F103C8T6 | 1 | Amazon | AliExpress |
| Wiznet W5500 | 1 | Amazon | AliExpress |
| ST-Link V2 | 1 | Amazon | AliExpress |
| Ethernet cable RJ-45 | 1 | Amazon | AliExpress |
| Breadboard Jumper set | 1 | Amazon | AliExpress |
| LED | 1 | Amazon | AliExpress |
| Resistor (1k Ohm) | 1 | Amazon | AliExpress |
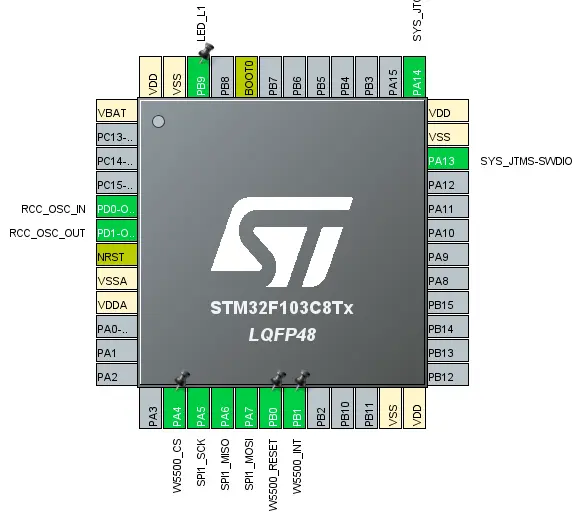
Pin Connections
| STM32F103C8T6 (Bluepill) | W5500 Module | ST Link V2 |
| PB0 | RST | – |
| PB1 | INT | – |
| PA6 | MISO | – |
| PA7 | MOSI | – |
| PA5 | SCLK | – |
| PA4 | CS | – |
| 3V3 (please use +3.3V external power Supply) | 3V3 (please use +3.3V external power Supply) | – |
| GND | GND | – |
| 3V3 (90 Degree Bent Pins) | 3V3 | |
| GND (90 Degree Bent Pins) | GND | |
| SWDIO (90 Degree Bent Pins) | SWDIO | |
| SCLK (90 Degree Bent Pins) | SCLK |
Then, connect the anode of an LED with a 1k resistor at PB9 and the other end to the ground
Please note: Power both the STM32F103C8T6 and the Wiznet W5500 Module from an external 3.3V power supply. In this, we used Stm32f103c8t6 internal power supply to power up the W5500 module, which is not a good practice and often causes hardware failure for Wiznet since it cannot run properly without enough current.
Preparing STM32CubeIDE
To create a project in STM32CubeIDE, please visit our previous tutorial. The link is given below:
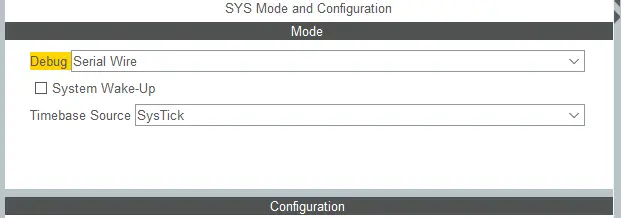
After creating the STM32CubeIDE project, from the CubeMX perspective, go to System core > sys, set ‘Serial Wire’ to the Debug drop-down menu
Also, go to System Core > RCC and set ‘Crystal/Ceramic Resonator’ to High Speed Clock (HSE)

Then, open the Clock Configuration setting and select the clock source HSI of 8 MHz and generate a 72MHz clock using the PLL of the STM32 microcontroller for the example project.
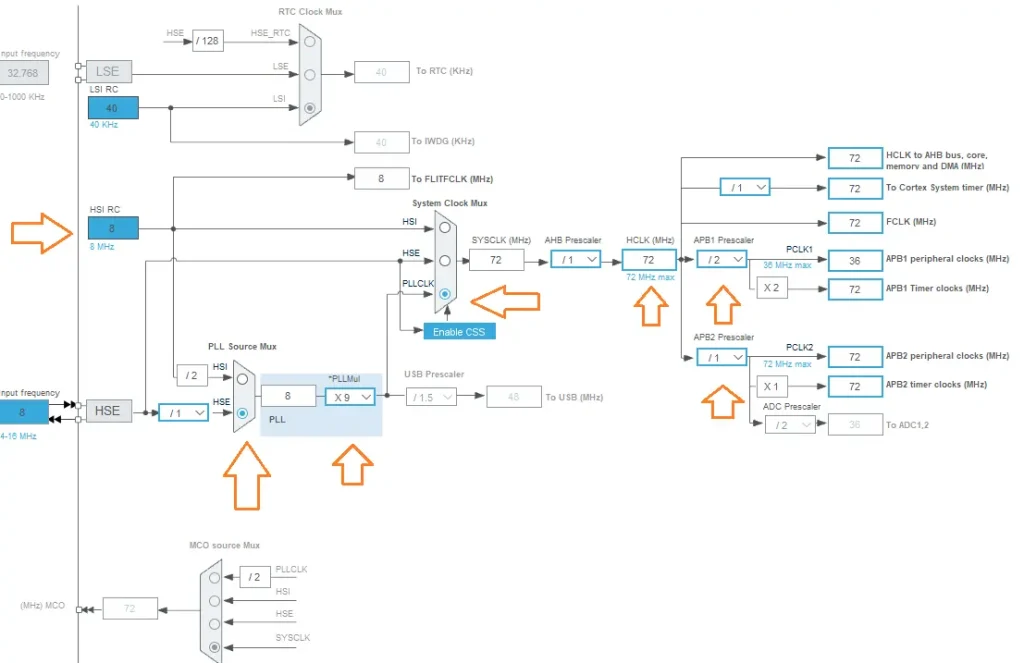
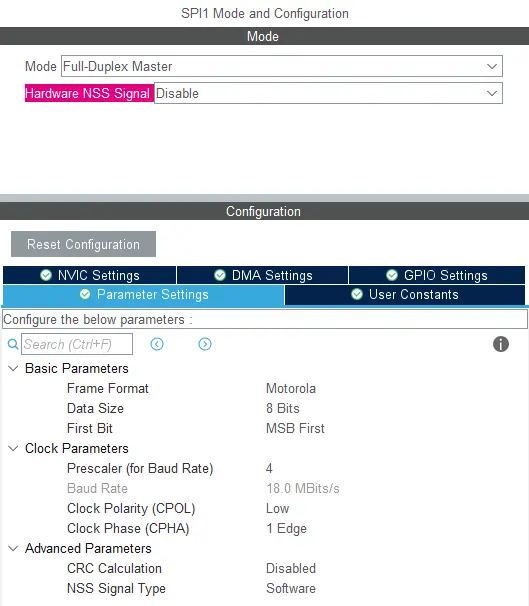
After that, click on the connectivity tab from the sidebar. Here we will use SPI1 for this project. Modify the SPI1 configuration according to the given screenshot below.
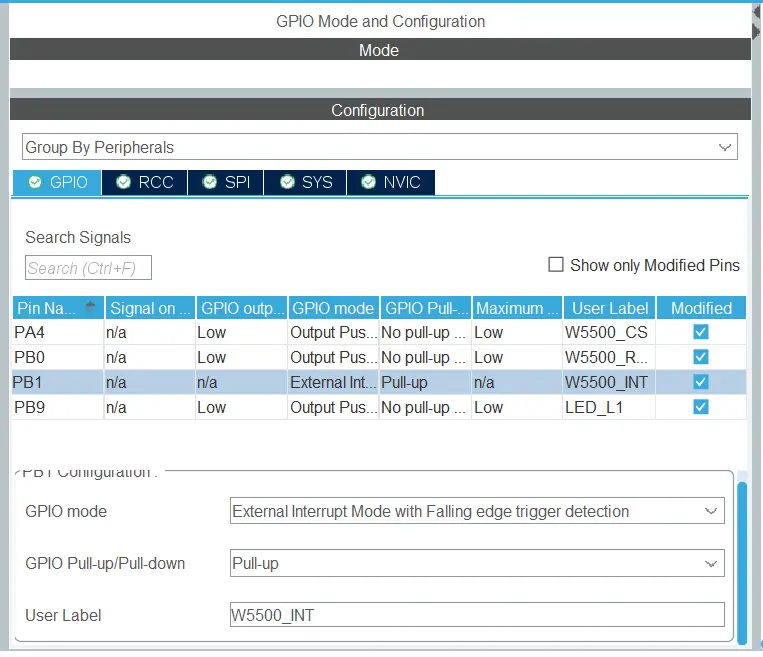
Then, in the pinout view, you will see some changes. Some changes have to be done by yourself. Here, left-clicking at PA4, PB0 and PB9, set it as GPIO OUTPUT. Moreover, you have to make PB1 as External Interrupt whose configuration will be “Pull up” and “External Interrupt mode with falling edge trigger”. Again Right right-clicking the pins, change the user label according to the screenshots given below. Then, press the code generation button, which looks like a little screw at the top left.
To make this project work, download the files from github links
- Wiznet Library
- Added Wiznet initialisation library
Add them to the project, and ensure that the source and include folder paths are included in the project. To do that, right-click on the project name > properties > C/C++ general > Paths and Symbols. It should look like this:
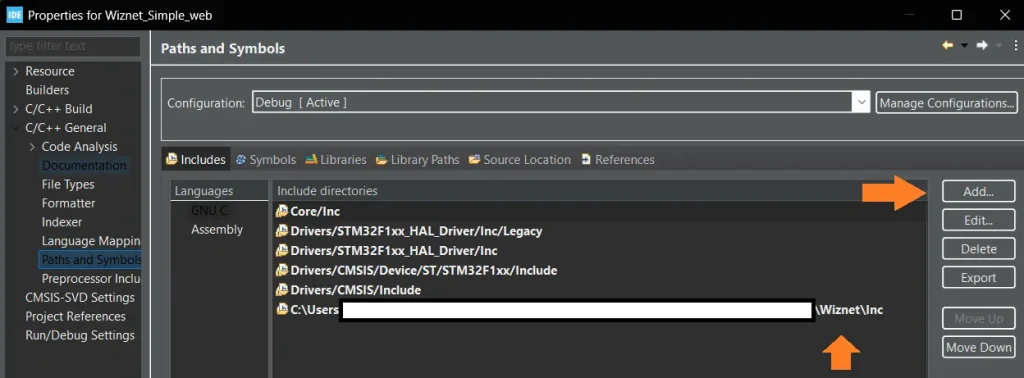
And
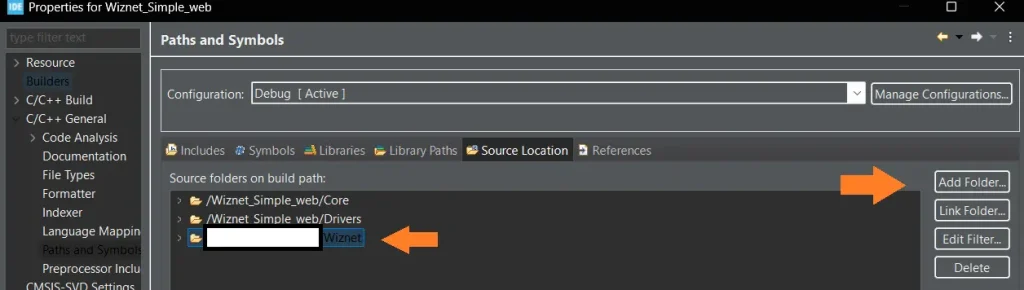
The sidebar of the project will look like this.
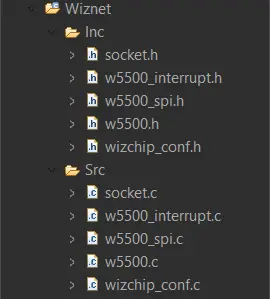
Code Explanation
void W5500_Enable_Interrupts(void) {
setIMR(IM_IR7 | IM_IR6 | IM_IR5 | IM_IR4); // Global interrupts
setSIMR(0xFF); // Enable socket interrupts for all sockets
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_SOCK_NUM; i++){
setSn_IMR(i, (Sn_IR_CON | Sn_IR_DISCON | Sn_IR_RECV | Sn_IR_TIMEOUT));
}
}
void W5500_InterruptHandler(void) {
for (uint8_t sn = 0; sn < MAX_SOCK_NUM; sn++) {
uint8_t ir = getSn_IR(sn);
if (ir) {
w5500_event_flags[sn].socket = sn;
w5500_event_flags[sn].connected = (ir & Sn_IR_CON) ? 1 : 0;
w5500_event_flags[sn].disconnected = (ir & Sn_IR_DISCON) ? 1 : 0;
w5500_event_flags[sn].received = (ir & Sn_IR_RECV) ? 1 : 0;
w5500_event_flags[sn].timeout = (ir & Sn_IR_TIMEOUT) ? 1 : 0;
w5500_event_flags[sn].sent = (ir & Sn_IR_SENDOK) ? 1 : 0;
setSn_IR(sn, ir); // Clear all flags that are set
}
}
}
void W5500_Handle_Events(void)
{
for (sn = 0; sn < MAX_SOCK_NUM; sn++) {
if (w5500_event_flags[sn].connected)
handle_connection(sn);
if (w5500_event_flags[sn].disconnected)
handle_disconnection(sn);
if (w5500_event_flags[sn].received)
handle_received(sn);
if (w5500_event_flags[sn].timeout)
handle_timeout(sn);
sock_status[sn] = getSn_SR(sn);
if (sock_status[sn] == SOCK_STATUS_CLOSE_WAIT || sock_status[sn] == SOCK_STATUS_CLOSED){
W5500_Close_Socket();
}
}
}
Here, all 8 of the sockets of the Wiznet are initialised in interrupt mode by manipulating the registers according to the dataset. Upon the wiznet trying to process something and trying to let the MCU know, it pulls down the interrupt pin. MCU, on the other hand, after getting an interrupt, executes a function that checks the state of a particular register (IR). The resister provides the condition of wiznet, i.e it receives data, sends data or initiates a connection, etc.
Another function, which is executed periodically in the main loop, checks the flag where the Wiznet state is stored. Based on the state, a particular function is executed.
For more information, see the video attached.
Full Code
main.c :
char sendBuffer[128];// Data holder
wiz_NetInfo netInfo = { .mac = { 0x00, 0x08, 0xdc, 0xab, 0xcd, 0xef }, .ip = {
192, 168, 20, 14 }, .sn = { 255, 255, 255, 0 }, .gw = { 192, 168, 20, 1 },
.dns = { 8, 8, 8, 8 }, .dhcp = NETINFO_STATIC };
uint8_t rrr = 0;
/* USER CODE END PV */
/* Private function prototypes -----------------------------------------------*/
void SystemClock_Config(void);
static void MX_GPIO_Init(void);
static void MX_SPI1_Init(void);
/* USER CODE BEGIN PFP */
/* USER CODE END PFP */
/* Private user code ---------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN 0 */
/* USER CODE END 0 */
/**
* @brief The application entry point.
* @retval int
*/
int main(void)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN 1 */
/* USER CODE END 1 */
/* MCU Configuration--------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Reset of all peripherals, Initializes the Flash interface and the Systick. */
HAL_Init();
/* USER CODE BEGIN Init */
/* USER CODE END Init */
/* Configure the system clock */
SystemClock_Config();
/* USER CODE BEGIN SysInit */
/* USER CODE END SysInit */
/* Initialize all configured peripherals */
MX_GPIO_Init();
MX_SPI1_Init();
/* USER CODE BEGIN 2 */
// HAL_GPIO_WritePin(LED_L1_GPIO_Port, LED_L1_Pin, SET);
W5500Init();
/* USER CODE END 2 */
/* Infinite loop */
/* USER CODE BEGIN WHILE */
while (1)
{
W5500_Handle_Events();
for (int socket_no = 0; socket_no < MAX_SOCK_NUM; socket_no++){
// Receive Data from PC and confirm the received Data by sending another message to PC
if (strncmp((char*)recv_buf[socket_no], "Hello", 5) == 0) {
memset(&recv_buf[socket_no], 0, sizeof(recv_buf[socket_no]));
snprintf(sendBuffer, sizeof(sendBuffer), "Received from %d\r\n", socket_no);
send(socket_no, (uint8_t*)sendBuffer, strlen(sendBuffer));
HAL_GPIO_TogglePin(LED_L1_GPIO_Port, LED_L1_Pin);
}
}
}
Please Note: Certain portions of the code, specifically those automatically generated by STM32CubeIDE, have been omitted.
main.h:
/* USER CODE BEGIN Header */
/**
******************************************************************************
* @file : main.h
* @brief : Header for main.c file.
* This file contains the common defines of the application.
******************************************************************************
* @attention
*
* Copyright (c) 2025 STMicroelectronics.
* All rights reserved.
*
* This software is licensed under terms that can be found in the LICENSE file
* in the root directory of this software component.
* If no LICENSE file comes with this software, it is provided AS-IS.
*
******************************************************************************
*/
/* USER CODE END Header */
/* Define to prevent recursive inclusion -------------------------------------*/
#ifndef __MAIN_H
#define __MAIN_H
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
#endif
/* Includes ------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#include "stm32f1xx_hal.h"
/* Private includes ----------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN Includes */
#include "wizchip_conf.h"
#include "socket.h"
#include "w5500_spi.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
/* USER CODE END Includes */
/* Exported types ------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN ET */
extern SPI_HandleTypeDef hspi1;
extern wiz_NetInfo netInfo;
/* USER CODE END ET */
/* Exported constants --------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN EC */
/* USER CODE END EC */
/* Exported macro ------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN EM */
/* USER CODE END EM */
/* Exported functions prototypes ---------------------------------------------*/
void Error_Handler(void);
/* USER CODE BEGIN EFP */
/* USER CODE END EFP */
/* Private defines -----------------------------------------------------------*/
#define W5500_CS_Pin GPIO_PIN_4
#define W5500_CS_GPIO_Port GPIOA
#define W5500_RESET_Pin GPIO_PIN_0
#define W5500_RESET_GPIO_Port GPIOB
#define W5500_INT_Pin GPIO_PIN_1
#define W5500_INT_GPIO_Port GPIOB
#define W5500_INT_EXTI_IRQn EXTI1_IRQn
#define LED_L1_Pin GPIO_PIN_9
#define LED_L1_GPIO_Port GPIOB
/* USER CODE BEGIN Private defines */
#define SERVER_PORT 8080
/* USER CODE END Private defines */
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
#endif /* __MAIN_H */
w5500_interrupt.c :
/*
* w5500_interrupt.c
*
* Created on: May 26, 2025
* Author: User
*/
#include <w5500_interrupt.h>
W5500_EventFlags w5500_event_flags[MAX_SOCK_NUM] = {0};
sock_state_t sock_status[MAX_SOCK_NUM];
uint8_t buf[32];
uint8_t recv_buf[MAX_SOCK_NUM][32] = {0};
uint8_t client_ip[MAX_SOCK_NUM][4] = {0};
uint8_t sn;
void HAL_GPIO_EXTI_Callback(uint16_t GPIO_Pin)
{
// static uint32_t last_interrupt_time = 0;
// uint32_t current_time = HAL_GetTick();
// Always handle W5500 interrupt immediately (no debounce)
if (GPIO_Pin == W5500_INT_Pin) {
W5500_InterruptHandler();
return;
}
}
void W5500_Init_Sockets(void) {
for (uint8_t sn = 0; sn < MAX_SOCK_NUM; sn++) {
if (socket(sn, Sn_MR_TCP, SERVER_PORT, 0) == sn) {
listen(sn);
}
}
}
void W5500_Close_Socket(void){
printf("Connection in closing state, restarting...\r\n");
disconnect(sn);
closesock(sn);
listen(sn);
}
// Interrupt Configuration
void W5500_Enable_Interrupts(void) {
setIMR(IM_IR7 | IM_IR6 | IM_IR5 | IM_IR4); // Global interrupts
setSIMR(0xFF); // Enable socket interrupts for all sockets
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_SOCK_NUM; i++){
setSn_IMR(i, (Sn_IR_CON | Sn_IR_DISCON | Sn_IR_RECV | Sn_IR_TIMEOUT));
}
}
void W5500_InterruptHandler(void) {
for (uint8_t sn = 0; sn < MAX_SOCK_NUM; sn++) {
uint8_t ir = getSn_IR(sn);
if (ir) {
w5500_event_flags[sn].socket = sn;
w5500_event_flags[sn].connected = (ir & Sn_IR_CON) ? 1 : 0;
w5500_event_flags[sn].disconnected = (ir & Sn_IR_DISCON) ? 1 : 0;
w5500_event_flags[sn].received = (ir & Sn_IR_RECV) ? 1 : 0;
w5500_event_flags[sn].timeout = (ir & Sn_IR_TIMEOUT) ? 1 : 0;
w5500_event_flags[sn].sent = (ir & Sn_IR_SENDOK) ? 1 : 0;
setSn_IR(sn, ir); // Clear all flags that are set
}
}
}
void W5500_Handle_Events(void)
{
for (sn = 0; sn < MAX_SOCK_NUM; sn++) {
if (w5500_event_flags[sn].connected)
handle_connection(sn);
if (w5500_event_flags[sn].disconnected)
handle_disconnection(sn);
if (w5500_event_flags[sn].received)
handle_received(sn);
if (w5500_event_flags[sn].timeout)
handle_timeout(sn);
sock_status[sn] = getSn_SR(sn);
if (sock_status[sn] == SOCK_STATUS_CLOSE_WAIT || sock_status[sn] == SOCK_STATUS_CLOSED){
W5500_Close_Socket();
}
}
}
void handle_connection(uint8_t sn) {
// Wait for established state before reading DIPR
if (getSn_SR(sn) == SOCK_ESTABLISHED) {
getSn_DIPR(sn, client_ip[sn]);
printf("Socket %d connected from %d.%d.%d.%d", sn,
client_ip[sn][0], client_ip[sn][1], client_ip[sn][2], client_ip[sn][3]);
} else {
memset(client_ip[sn], 0, 4);
printf("Socket %d connection event, but not established ", sn);
}
memset(&w5500_event_flags[sn], 0, sizeof(W5500_EventFlags));
}
void handle_received(uint8_t sn) {
int32_t size = getSn_RX_RSR(sn);
if (size > 0 && size < sizeof(recv_buf[sn])) {
int32_t len = recv(sn, recv_buf[sn], size);
if (len > 0) {
recv_buf[sn][len] = '\0';
// recv_buf[sn]
}
}
memset(&w5500_event_flags[sn], 0, sizeof(W5500_EventFlags));
}
void handle_sent(uint8_t sn) {
printf("Data sent on socket %d\n", sn);
memset(&w5500_event_flags[sn], 0, sizeof(W5500_EventFlags));
}
void handle_disconnection(uint8_t sn) {
printf("Socket %d disconnected ", sn);
memset(client_ip[sn], 0, 4); // Reset client IP on disconnection
disconnect(sn);
closesock(sn);
socket(sn, Sn_MR_TCP, SERVER_PORT, 0);
listen(sn);
memset(&w5500_event_flags[sn], 0, sizeof(W5500_EventFlags));
}
void handle_timeout(uint8_t sn) {
printf("Timeout on socket %d\n", sn);
disconnect(sn);
closesock(sn);
socket(sn, Sn_MR_TCP, SERVER_PORT, 0);
listen(sn);
memset(&w5500_event_flags[sn], 0, sizeof(W5500_EventFlags));
}
int8_t SendToSocket(uint8_t sn, const char *msg)
{
if (getSn_SR(sn) == SOCK_ESTABLISHED) {
int32_t result = send(sn, (uint8_t *)msg, strlen(msg));
if (result > 0) {
printf("Sent on socket %d: %s\n", sn, msg);
return 0; // Success
}
else
{
printf("Failed to send on socket %d\n ", sn);
return -2; // Send error
}
} else {
printf("Socket %d not connected\n", sn);
return -1; // Socket not established
}
}
w5500_interrupt.h :
/*
* w5500_interrupt.h
*
* Created on: May 26, 2025
* Author: User
*/
#ifndef INC_W5500_INTERRUPT_H_
#define INC_W5500_INTERRUPT_H_
#include "main.h"
#include "socket.h"
#include "w5500.h"
#include "w5500_spi.h"
#define MAX_SOCK_NUM 8
extern uint8_t sn;
extern uint8_t recv_buf[MAX_SOCK_NUM][32];
typedef struct {
uint8_t socket;
uint8_t connected;
uint8_t disconnected;
uint8_t received;
uint8_t timeout;
uint8_t sent;
} W5500_EventFlags;
extern W5500_EventFlags w5500_event_flags[];
typedef enum {
SOCK_STATUS_CLOSED = 0x00,
SOCK_STATUS_INIT = 0x13,
SOCK_STATUS_LISTEN = 0x14,
SOCK_STATUS_ESTABLISHED = 0x17,
SOCK_STATUS_CLOSE_WAIT = 0x1C,
SOCK_STATUS_FIN_WAIT = 0x18,
SOCK_STATUS_TIME_WAIT = 0x1B,
SOCK_STATUS_ERROR = 0xFF
} sock_state_t;
extern sock_state_t sock_status[MAX_SOCK_NUM];
//void process_received_command(uint8_t sn, const char *buffer);
void W5500_Init_Sockets(void);
void W5500_Close_Socket(void);
void W5500_Enable_Interrupts(void);
void W5500_InterruptHandler(void);
void W5500_Handle_Events(void);
void handle_connection(uint8_t sn);
void handle_received(uint8_t sn);
void handle_sent(uint8_t sn);
void handle_disconnection(uint8_t sn);
void handle_timeout(uint8_t sn);
int8_t SendToSocket(uint8_t sn, const char *msg);
#endif /* INC_W5500_INTERRUPT_H_ */
W5500_spi.c :
#include "w5500_spi.h"
SPI_HandleTypeDef *spi_handle = &hspi1;
void mcu_cris_enter(void) {
__set_PRIMASK(1);
}
void mcu_cris_exit(void) {
__set_PRIMASK(0);
}
void wizchip_select(void) {
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(W5500_CS_GPIO_Port, W5500_CS_Pin, GPIO_PIN_RESET);
}
void wizchip_deselect(void) {
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(W5500_CS_GPIO_Port, W5500_CS_Pin, GPIO_PIN_SET);
}
uint8_t wizchip_read() {
uint8_t rbuf;
HAL_SPI_Receive(spi_handle, &rbuf, 1, 100);
return rbuf;
}
void wizchip_write(uint8_t wb) {
HAL_SPI_Transmit(spi_handle, &wb, 1, 100);
}
void wizchip_readburst(uint8_t* pBuf, uint16_t len) {
for (uint16_t i=0; i<len; i++) {
*pBuf = wizchip_read();
pBuf++;
}
}
void wizchip_writeburst(uint8_t* pBuf, uint16_t len) {
for (uint16_t i=0; i<len; i++){
wizchip_write(*pBuf);
pBuf++;
}
}
void W5500Init() {
uint8_t tmp;
// initialize the buffers, 2kb for each socket
uint8_t memsize[2][8] = {{4,2,2,2, 2,2,1,1}, {4,2,2,2, 2,2,1,1}};
// CS high by default, not selected by default
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(W5500_CS_GPIO_Port, W5500_CS_Pin, GPIO_PIN_SET);
// give the reset pin a brief pulse, to reset everything
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(W5500_RESET_GPIO_Port, W5500_RESET_Pin, GPIO_PIN_RESET);
tmp = 0xFF;
while(tmp--);
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(W5500_RESET_GPIO_Port, W5500_RESET_Pin, GPIO_PIN_SET);
// point to the mcu specific functions
reg_wizchip_cris_cbfunc(mcu_cris_enter, mcu_cris_exit);
reg_wizchip_cs_cbfunc(wizchip_select, wizchip_deselect);
reg_wizchip_spi_cbfunc(wizchip_read, wizchip_write);
reg_wizchip_spiburst_cbfunc(wizchip_readburst, wizchip_writeburst);
// wizchip initialize
if (ctlwizchip(CW_INIT_WIZCHIP, (void*)memsize) == -1) {
while(1);
// @todo: handle this failed init case.
}
wizchip_setnetinfo(&netInfo);
wizchip_getnetinfo(&netInfo);
}
W5500_spi.h :
#ifndef INC_W5500_SPI_H_ #define INC_W5500_SPI_H_ #include "main.h" extern SPI_HandleTypeDef *spi_handle; void W5500Init(void); #endif /* INC_W5500_SPI_H_ */
